What is cement?
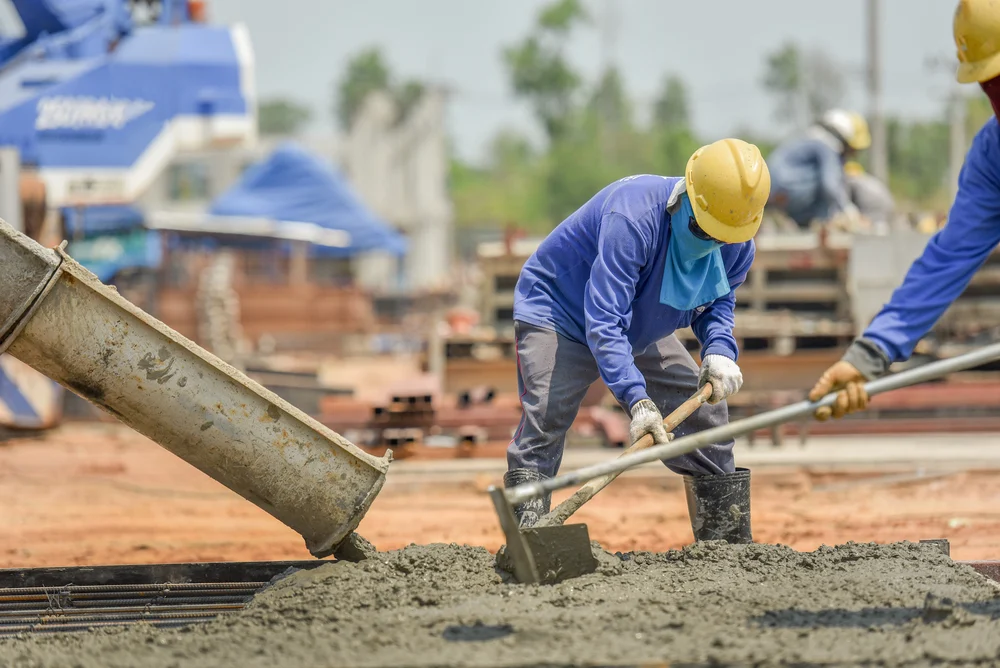
Cement is used in construction to bind different materials together. The majority of its ingredients, which include clay, limestone, and other minerals, are burnt at high temperatures in a kiln to undergo a chemical process called calcination, resulting in a fine powder. Clinker is produced by this process, which is then ground into a fine powder
Because of its cohesive and adhesive properties, cement may unite fragments of minerals into a compact whole.
✏ It is an essential binding material used in almost all disciplines related to building.
✏ Cement is resistant to severe weather, such as precipitation, wind, and snow. It also has corrosion resistance and resistance to environmental factors.
It is also very resistant to water, which makes it ideal for use in the construction of watertight containers such as sewage and water tanks. Cement is also often used to create patios, driveways, and other decorative features.
✏ Cement is a great material to employ for construction, particularly high-rise structures, since it doesn’t burn. Its non-burning nature makes it a useful component for firewalls, since it may help confine flames. It works well as an insulator as well.
Regarding costs, cement manufacture is rather inexpensive. The price may vary according on the sort, aggregate quality, and necessary transportation. But it’s generally less expensive when compared to other building materials like steel and wood.
Uses of cement
Cement is now widely used in the construction of various technological structures all over the world. It has established itself as one of the most cutting-edge technological materials of the modern period and is unparalleled in both manufacture and applications. Cement is most often used as mortar and concrete, where it is mixed with aggregate, an inert material, to make a strong binding substance. It may also be used “neat,” or as grouting material on its own. A few possible uses or applications for cement are as follows:
- Cement is mostly used to make mortar and concrete.
- Cement mortar is used in masonry building, pointing, and plastering.
- For instance, pillars, stairs, weather shelters, lintels, beams, and roofs may all be constructed using cement concrete.
- It may be used to construct significant engineering structures including docks, storage reservoirs, bridges, culverts, dams, tunnels, lighthouses, etc.
- It may also be used to construct water tanks, septic tanks, lamp poles, tennis courts, telephone cabins, and roads.
- It is used in the construction of joints in drains, pipelines, and other systems.
- It may be used to make precast pipes, garden seats, ornamental urns, flower pots, dust bins, fence posts, and other things.
- It may be used to waterproof floors, foundations, paths, etc.
- It may be used to create fire-resistant concrete structures. It may also be used to the creation of acid- and waterproof structures.
- Colored cement may be used to adorn or color the constructions.
- It may be used to shotcrete the geological walls of the tunnel to reinforce the construction.
- Despite having many uses, cement has few disadvantages. However, its benefits far exceed its downsides. Among the disadvantages of cement are the following:
Cement-based constructions are difficult to disassemble or repurpose once built. Compared to steel or plastic, they are less easily recycled.
Concrete buildings have a high weight. Consequently, skyscrapers cannot be built entirely of cement. Instead, steel buildings are erected.
uses for various kind of cement
1. Use of Ordinary Portland Cement:
- It is a good fit for use in typical concrete construction projects, such building flyovers, roads, bridges, dams, and tall buildings.
- Grouts and mortars are made using it.
2. Use of Modified Portland Cement:
- Because of its lower heat of hydration, it may be used in hot climates and for the construction of large piers, retaining walls, heavy abutments, etc., provided that the sulphate content is not too high.
3. Use of Rapid hardening Portland cement :
- It is used in circumstances where quick strength development is required, such as when the framework must be disassembled quickly for reuse or when it must get sufficient strength quickly to allow for further construction.
4. Use of Extra rapid hardening cement uses:
- It is effective when concreting in cold weather or when very high early strength is required; nevertheless, under these circumstances, it is not recommended to use aluminous cement.
5. Use of low-heat Portland cement:
- This particular kind of cement is used because it generates a lot of heat when the cement sets.
- Its main use is mass concrete work.
6. Use of sulphur-resistant Portland cement:
- It is used in areas where the sulfate impact is considerable.
- It is used to structures that are likely damaged by very alkaline conditions, such as canal linings, culverts, siphons, etc.
7. Use of Water-repellent Portland cement:
- The majority of applications for this kind of cement include waterproof renderings, colored renderings, and stucco, which are utilized to identify moisture incursion in basements.
8. Use of Water-impervious Portland cement:
- It is used in the construction of water-retaining structures, including as retaining walls, bridges, tanks, reservoirs, dams, and swimming pools.
Other varieties of cement
1. High-alumina cement
- a. It is used in chemical plants and furnaces.
- b. It is used during emergency situations involving conflicts and in colder climates with temperatures of eighteen degrees Celsius or below.
- c. It is used in underwater structures.
2. Quick setting cement
- Due to its quick-setting nature, it is used in projects where concrete is immersed or in flowing water.
3. Blast furnace slag cement
- This kind of cement may be employed in large-scale concrete projects since it hydrates at a lower temperature than ordinary Portland cement.
- However, because to the low heat of hydration of blast-furnace slag cement and a relatively sluggish rate of strength expansion, frost damage may occur in cold weather. This kind of cement should not be used in thin R.C.C. buildings.
- This kind of cement is often used in marine construction due to its comparatively good sulfate resistance.
4. White Cement
- It is used in many different areas of building construction, including as plastering, floor finishing, ornamental components, etc.
- It may also be used as marble and tile mortar.
- White cement is also used for many other things, such shaping statues and sculptures, painting garden furniture, and changing out glazed pool tiles with vibrant, underwater-friendly paints.
- Ready-mixed concrete and precast concrete blocks are also used with it.
5. Color cement
- A lot of external surfaces, floors, stair treads, window sill slabs, textured panel faces, and imitation marble are finished with these types of cement.
6. Acid-resistant cement
- It offers coatings that are resistant to heat and acid for use in the chemical sector.
7. Expanding cement
- Typically used in the building of structures designed to contain water.
- Damaged concrete surfaces are also repaired using it.
8. Hydrophobic cement
- When this cement is used to produce concrete, the tiny pores are distributed equally. This gives such concrete a far stronger resilience to frost and water.
9. Portland Cement Pozzolana
- It finds widespread use in hydraulic projects, or mass concrete works, such as dams and weirs.
- Submerged construction projects, such those constructing sewage systems, also use it.
10. Supersulphate cement
- This cement may be used wherever that other types of cement are used, except from very hot environments.
- It has been used to the undersides of bridges, train tracks, and concrete sewers that convey industrial effluents.