There are several types of irrigation systems available. Irrigation uses both groundwater and surface water. An irrigation system may be classified as:
- Using Water Powered by Gravity to Water
- Pumped Irrigation
- Tidal Irrigation
1. Using Water Powered by Gravity to Water
When using a gravity irrigation system, water is exclusively moved by gravity to the field. This kind of irrigation system consists of headworks across the river and a network of canals that distributes water. Water is routinely delivered by the canals in accordance with agricultural needs and water availability. It may also be separated into two groups: storage systems and run-of-the-river projects.
Plan for Flow-of-the-River
By using a weir or barrage to bridge the river, this technique elevates the water level to the point where the flow is directed into the canal system. A run-of-the-river plan directs the river’s daily flow into the system of canals, with a maximum discharge limit determined by the canal’s head capacity. Two examples of this scheme are the Ganga Canal System in Uttar Pradesh and the Sharda Canal System in the state of Uttar Pradesh; in both cases, the excess river discharge is allowed to flow downstream.
Technique for storing
A dam is constructed in a storage system, like the Bhakra Dam scheme in H.P./Punjab and the Ramganga project in the UK/UP, to store water during the monsoon and utilize it as a source of water supply in canals for agricultural and power requirements.
Since the river flow is retained in the reservoir and released in line with irrigation demand, it is evident that a storage system makes more optimum use of available water resources than a run-of-the-river plan. Plans for storing water, however, are more costly and are to be used only in situations where the water can be reused again.
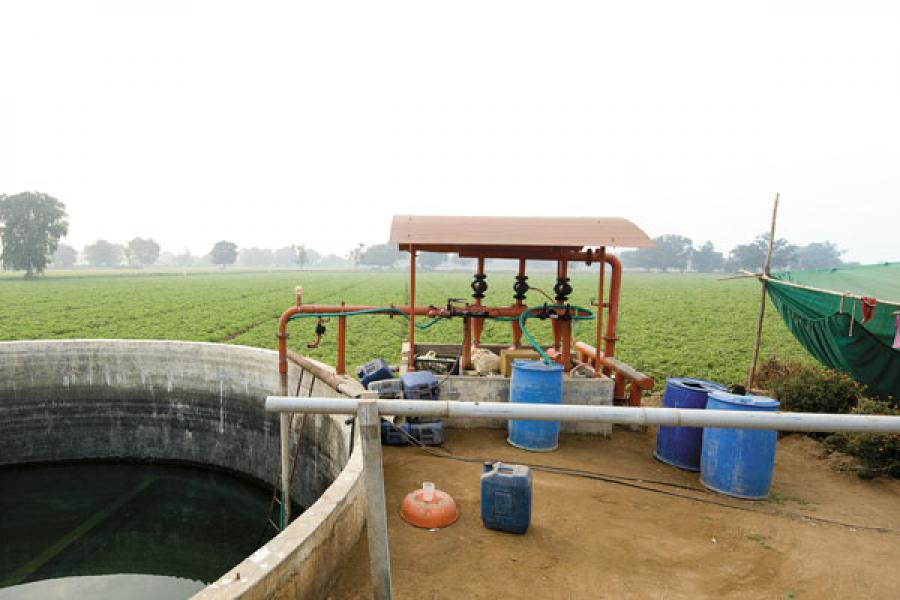
2. Pumped Irrigation
This kind of irrigation system, which may be split into two categories—pumped irrigation from surface water and pumped irrigation from ground water—uses pumps to increase the water level. An irrigation scheme that pumps surface water is known as lift irrigation; tube-well irrigation is the term for this kind of irrigation.
Increase Watering
This scheme makes use of water from quite big rivers. When constructing a barrage or weir is judged impractical due to their high cost, the strategy is used. Lift irrigation to higher-up service points may also be a part of a gravity canal system.
A novel approach to pump house design has been developed in UP. With this method, pumps are installed atop big floating barges. Since the location and height of the barges may be changed, water supply is ensured throughout the whole river system.
Watering Using Tubes in Wells
In the settlements, water is still often extracted from wells for irrigation using antiquated methods. These days, they are gradually being replaced by pumps and tube-wells.
Utilizing groundwater resources via tube-well technology is the most economical method. As the name implies, water is retrieved by placing a pump in a small hole that is excavated well below the surface.
3. Tidal Irrigation
A tidal irrigation design submerges the watered area during periods of high river flows during the monsoon. With this setup, the river’s flow volume cannot be controlled. When rainfall or little irrigation is paired with the moisture that has been retained in the soil due to floods, the crops attain maturity. It’s also known as flood irrigation.
4. Alternative methods for irrigation
Various watering strategies are used in certain places. In undulating terrain, tanks or bunds are constructed to collect rainfall. These bunds discharge water for agriculture during the non-monsoon season. In the deltaic region, delta irrigation is used. During floods, temporary headworks are constructed using this method to divert water to land.